IFNA function in Excel
Use the IFNA function in Excel to replace a #N/A error with a friendly message. The IFNA function only catches #N/A errors.
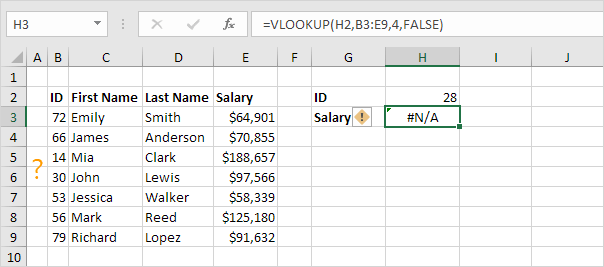
1. For example, Excel returns the #N/A error when the VLOOKUP function cannot find a match.
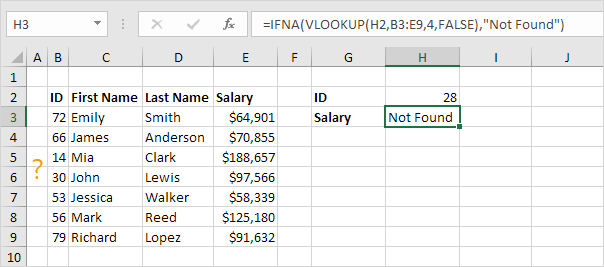
2. Use the IFNA function to replace the #N/A error with a friendly message.
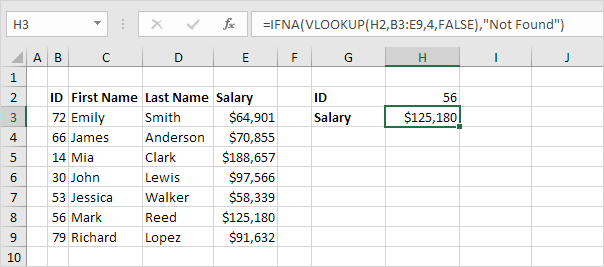
3. If the VLOOKUP function does not evaluate to a #N/A error, the IFNA function simply returns the result of the VLOOKUP function.
The IFNA function was introduced in Excel 2013. If you're using Excel 2010 or Excel 2007, combine IF and ISNA (step 5) or use IFERROR (step 6).
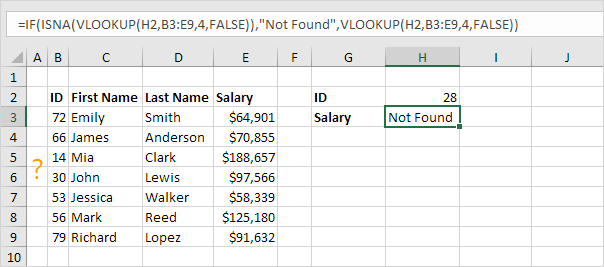
4. First, the ISNA function checks whether a value is #N/A, and returns TRUE or FALSE.
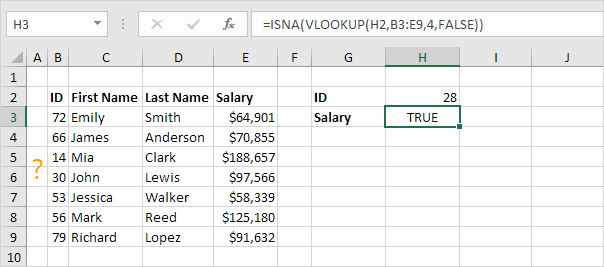
5. Combine IF and ISNA.
6. The previous formula is quite long. You can also use the IFERROR function in Excel.
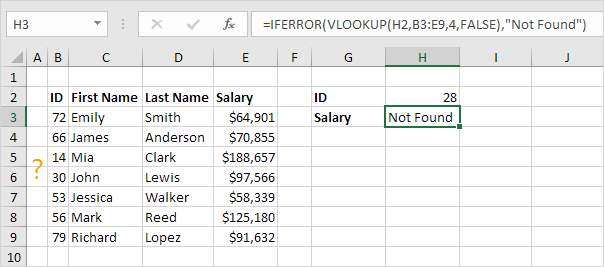
Note: the IFERROR function catches other errors as well. For example, the #NAME? error if you accidentally misspell the word VLOOKUP.